Get Started with Istio Ambient Mesh
Step by step guide to get started with Istio ambient mesh.
Ambient mesh is a new data plane mode for Istio introduced today. Following this getting started guide, you can experience how ambient mesh can simplify your application onboarding, help with ongoing operations, and reduce service mesh infrastructure resource usage.
Install Istio with Ambient Mode
- Download the preview version of Istio with support for ambient mesh.
- Check out supported environments. We recommend using a Kubernetes cluster that is version 1.21 or newer that has two nodes or more. If you don’t have a Kubernetes cluster, you can set up using locally (e.g. using kind as below) or deploy one in Google or AWS Cloud:
$ kind create cluster --config=- <<EOF
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
name: ambient
nodes:
- role: control-plane
- role: worker
- role: worker
EOF
The ambient profile is designed to help you get started with ambient mesh.
Install Istio with the ambient profile on your Kubernetes cluster, using the istioctl downloaded above:
$ istioctl install --set profile=ambient
After running the above command, you’ll get the following output that indicates these four components are installed successfully!
✔ Istio core installed
✔ Istiod installed
✔ Ingress gateways installed
✔ CNI installed
✔ Installation complete
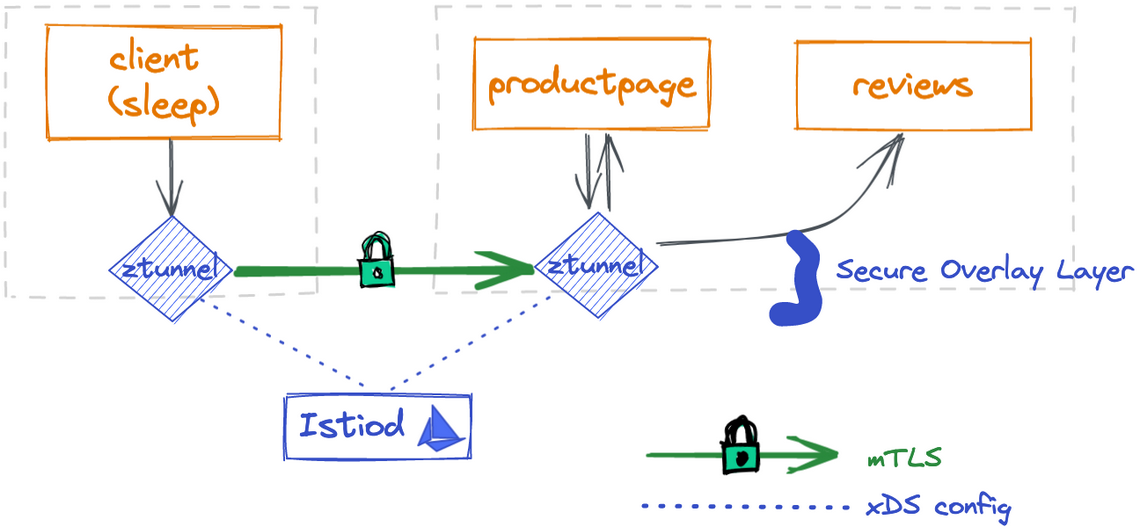
By default, the ambient profile has the Istio core, Istiod, ingress gateway, zero-trust tunnel agent (ztunnel) and CNI plugin enabled. The Istio CNI plugin is responsible for detecting which application pods are part of the ambient mesh and configuring the traffic redirection between the ztunnels. You’ll notice the following pods are installed in the istio-system namespace with the default ambient profile:
$ kubectl get pod -n istio-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
istio-cni-node-97p9l 1/1 Running 0 29s
istio-cni-node-rtnvr 1/1 Running 0 29s
istio-cni-node-vkqzv 1/1 Running 0 29s
istio-ingressgateway-5dc9759c74-xlp2j 1/1 Running 0 29s
istiod-64f6d7db7c-dq8lt 1/1 Running 0 47s
ztunnel-bq6w2 1/1 Running 0 47s
ztunnel-tcn4m 1/1 Running 0 47s
ztunnel-tm9zl 1/1 Running 0 47s
The istio-cni and ztunnel components are deployed as Kubernetes DaemonSets which run on every node.
Each Istio CNI pod checks all pods co-located on the same node to see if these pods are part of the ambient mesh.
For those pods, the CNI plugin configures traffic redirection so that all incoming and outgoing traffic to the pods are redirected to the co-located ztunnel first.
As new pods are deployed or removed on the node, CNI plugin continues to monitor and update the redirection logic accordingly.
Deploy Your Applications
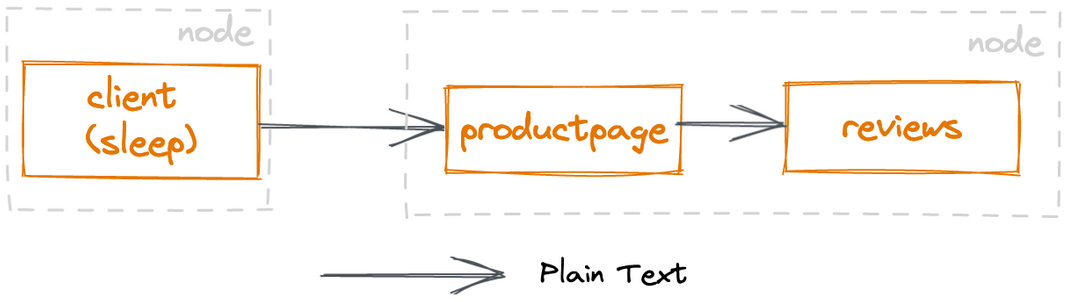
You’ll use the sample bookinfo application, which is part of your Istio download from previous steps. In ambient mode, you deploy applications to your Kubernetes cluster exactly the same way you would without Istio. This means you can have your applications running in your Kubernetes before you enable ambient mesh, and have them join the mesh without needing to restart or reconfigure your applications.
$ kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/linsun/sample-apps/main/sleep/sleep.yaml
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/linsun/sample-apps/main/sleep/notsleep.yaml
Note: sleep and notsleep are two simple applications that can serve as curl clients.
Connect productpage to the Istio ingress gateway so you can access the bookinfo app from outside of the cluster:
$ kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
Test your bookinfo application, it should work with or without the gateway. Note: you can replace istio-ingressgateway.istio-system below with its load balancer IP (or hostname) if it has one:
$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- curl -s http://istio-ingressgateway.istio-system/productpage | head -n1
$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/ | head -n1
$ kubectl exec deploy/notsleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/ | head -n1
Adding your application to the ambient mesh
You can enable all pods in a given namespace to be part of the ambient mesh by simply labeling the namespace:
$ kubectl label namespace default istio.io/dataplane-mode=ambient
Congratulations! You have successfully added all pods in the default namespace to the ambient mesh. The best part is that there is no need to restart or redeploy anything!
Send some test traffic:
$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- curl -s http://istio-ingressgateway.istio-system/productpage | head -n1
$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/ | head -n1
$ kubectl exec deploy/notsleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/ | head -n1
You’ll immediately gain mTLS communication among the applications in the Ambient mesh.
If you are curious about the X.509 certificate for each identity, you can learn more about it by stepping through a certificate:
$ istioctl pc secret ds/ztunnel -n istio-system -o json | jq -r '.dynamicActiveSecrets[0].secret.tlsCertificate.certificateChain.inlineBytes' | base64 --decode | openssl x509 -noout -text -in /dev/stdin
For example, the output shows the certificate for the sleep principle that is valid for 24 hours, issued by the local Kubernetes cluster.
Certificate:
Data:
Version: 3 (0x2)
Serial Number: 307564724378612391645160879542592778778 (0xe762cfae32a3b8e3e50cb9abad32b21a)
Signature Algorithm: SHA256-RSA
Issuer: O=cluster.local
Validity
Not Before: Aug 29 21:00:14 2022 UTC
Not After : Aug 30 21:02:14 2022 UTC
Subject:
Subject Public Key Info:
Public Key Algorithm: RSA
Public-Key: (2048 bit)
Modulus:
ac:db:1a:77:72:8a:99:28:4a:0c:7e:43:fa:ff:35:
75:aa:88:4b:80:4f:86:ca:69:59:1c:b5:16:7b:71:
dd:74:57:e2:bc:cf:ed:29:7d:7b:fa:a2:c9:06:e6:
d6:41:43:2a:3c:2c:18:8e:e8:17:f6:82:7a:64:5f:
c4:8a:a4:cd:f1:4a:9c:3f:e0:cc:c5:d5:79:49:37:
30:10:1b:97:94:2c:b7:1b:ed:a2:62:d9:3b:cd:3b:
12:c9:b2:6c:3c:2c:ac:54:5b:a7:79:97:fb:55:89:
ca:08:0e:2e:2a:b8:d2:e0:3b:df:b2:21:99:06:1b:
60:0d:e8:9d:91:dc:93:2f:7c:27:af:3e:fc:42:99:
69:03:9c:05:0b:c2:11:25:1f:71:f0:8a:b1:da:4a:
da:11:7c:b4:14:df:6e:75:38:55:29:53:63:f5:56:
15:d9:6f:e6:eb:be:61:e4:ce:4b:2a:f9:cb:a6:7f:
84:b7:4c:e4:39:c1:4b:1b:d4:4c:70:ac:98:95:fe:
3e:ea:5a:2c:6c:12:7d:4e:24:ab:dc:0e:8f:bc:88:
02:f2:66:c9:12:f0:f7:9e:23:c9:e2:4d:87:75:b8:
17:97:3c:96:83:84:3f:d1:02:6d:1c:17:1a:43:ce:
68:e2:f3:d7:dd:9e:a6:7d:d3:12:aa:f5:62:91:d9:
8d
Exponent: 65537 (0x10001)
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Key Usage: critical
Digital Signature, Key Encipherment
X509v3 Extended Key Usage:
Server Authentication, Client Authentication
X509v3 Basic Constraints: critical
CA:FALSE
X509v3 Authority Key Identifier:
keyid:93:49:C1:B8:AB:BF:0F:7D:44:69:5A:C3:2A:7A:3C:79:19:BE:6A:B7
X509v3 Subject Alternative Name: critical
URI:spiffe://cluster.local/ns/default/sa/sleep
Note: If you don’t get any output, it may mean ds/ztunnel has selected a node that doesn’t manage any certificates. You can specify a specific ztunnel pod (e.g. istioctl pc secret ztunnel-tcn4m -n istio-system) that manages either one of the sample application pods instead.
Secure application access
After you have added your application to ambient mesh, you can secure application access using L4 authorization policies.
This lets you control access to and from a service based on client workload identities, but not at the L7 level, such as HTTP methods like GET and POST.
L4 Authorization Policies
Explicitly allow the sleep service account and istio-ingressgateway service accounts to call the productpage service:
$ kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: productpage-viewer
namespace: default
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: productpage
action: ALLOW
rules:
- from:
- source:
principals: ["cluster.local/ns/default/sa/sleep", "cluster.local/ns/istio-system/sa/istio-ingressgateway-service-account"]
EOF
Confirm the above authorization policy is working:
$ # this should succeed
$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- curl -s http://istio-ingressgateway.istio-system/productpage | head -n1
$ # this should succeed
$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/ | head -n1
$ # this should fail with an empty reply
$ kubectl exec deploy/notsleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/ | head -n1
Layer 7 Authorization Policies
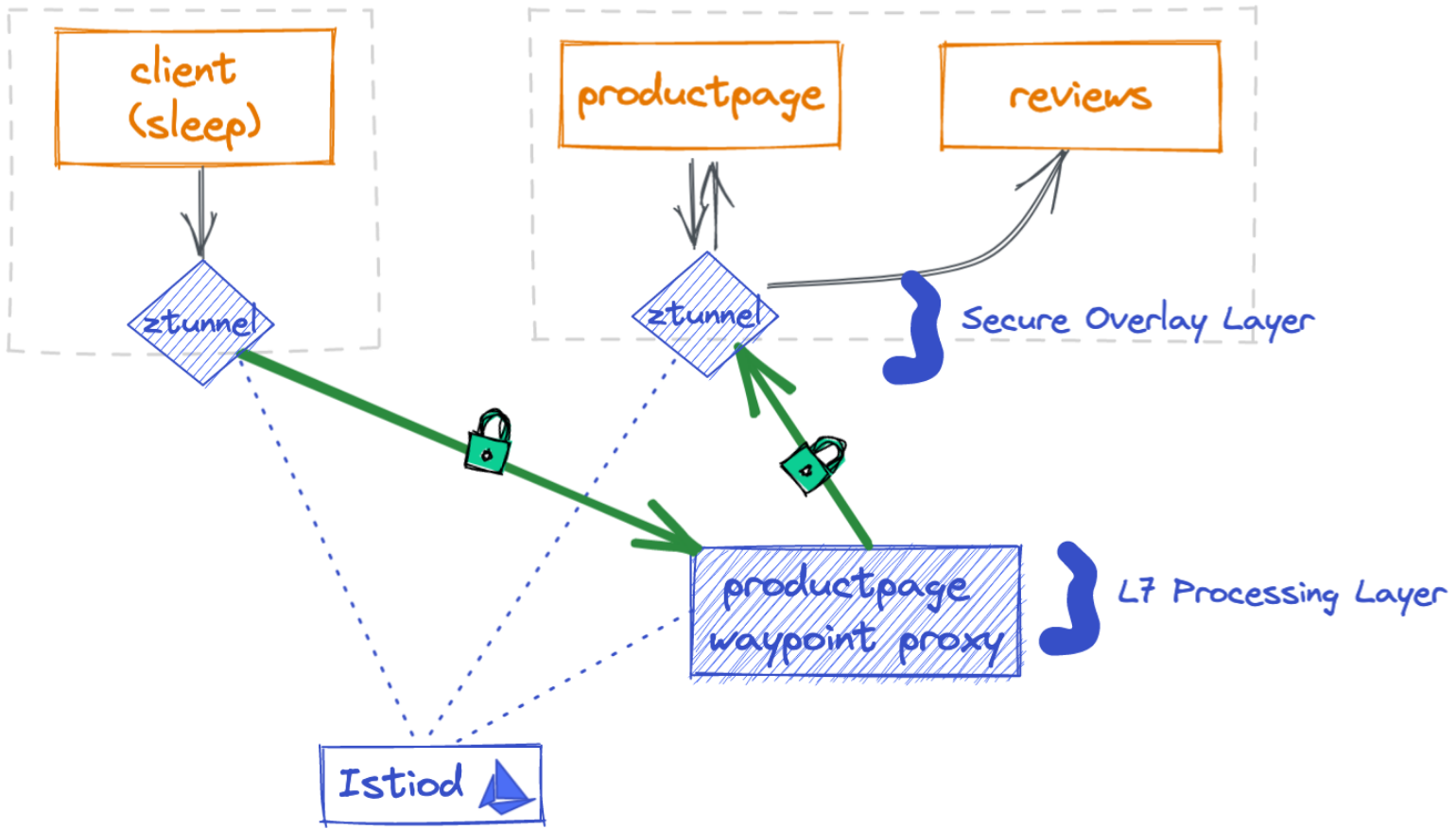
Using the Kubernetes Gateway API, you can deploy a waypoint proxy for the productpage service that uses the bookinfo-productpage service account. Any traffic going to the productpage service will be mediated, enforced and observed by the Layer 7 (L7) proxy.
$ kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: productpage
annotations:
istio.io/service-account: bookinfo-productpage
spec:
gatewayClassName: istio-mesh
EOF
Note the gatewayClassName has to be istio-mesh for the waypoint proxy.
View the productpage waypoint proxy status; you should see the details of the gateway resource with Ready status:
$ kubectl get gateway productpage -o yaml
...
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2022-09-06T20:24:41Z"
message: Deployed waypoint proxy to "default" namespace for "bookinfo-productpage"
service account
observedGeneration: 1
reason: Ready
status: "True"
type: Ready
Update our AuthorizationPolicy to explicitly allow the sleep service account and istio-ingressgateway service accounts to GET the productpage service, but perform no other operations:
$ kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: productpage-viewer
namespace: default
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: productpage
action: ALLOW
rules:
- from:
- source:
principals: ["cluster.local/ns/default/sa/sleep", "cluster.local/ns/istio-system/sa/istio-ingressgateway-service-account"]
to:
- operation:
methods: ["GET"]
EOF
Confirm the above authorization policy is working:
$ # this should fail with an RBAC error because it is not a GET operation
$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/ -X DELETE | head -n1
$ # this should fail with an RBAC error because the identity is not allowed
$ kubectl exec deploy/notsleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/ | head -n1
$ # this should continue to work
$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/ | head -n1
With the productpage waypoint proxy deployed, you’ll also automatically get L7 metrics for all requests to the productpage service:
$ kubectl exec deploy/bookinfo-productpage-waypoint-proxy -- curl -s http://localhost:15020/stats/prometheus | grep istio_requests_total
You’ll notice the metric with response_code=403 and some metrics response_code=200, like below:
istio_requests_total{
response_code="403",
source_workload="notsleep",
source_workload_namespace="default",
source_principal="spiffe://cluster.local/ns/default/sa/notsleep",
destination_workload="productpage-v1",
destination_principal="spiffe://cluster.local/ns/default/sa/bookinfo-productpage",
connection_security_policy="mutual_tls",
...
}
The metric shows two 403 responses when the source workload (notsleep) calls the destination workload(productpage-v1) along with source and destination principals via mutual TLS connection.
Control Traffic
Deploy a waypoint proxy for the review service, using the bookinfo-review service account, so that any traffic going to the review service will be mediated by the waypoint proxy.
$ kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: reviews
annotations:
istio.io/service-account: bookinfo-reviews
spec:
gatewayClassName: istio-mesh
EOF
Apply the reviews virtual service to control 90% traffic to reviews v1 and 10% traffic to reviews v2.
$ kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-reviews-90-10.yaml
$ kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/destination-rule-reviews.yaml
Confirm that roughly 10% traffic from the 100 requests go to reviews-v2:
$ kubectl exec -it deploy/sleep -- sh -c 'for i in $(seq 1 100); do curl -s http://istio-ingressgateway.istio-system/productpage | grep reviews-v.-; done'
Wrapping up
The existing Istio resources continue to work, regardless if you choose to use the sidecar or ambient data plane mode.
Take a look at the short video to watch Lin run through the Istio ambient mesh demo in 5 minutes:
What’s next
We are super excited about the new Istio ambient data plane with its simple “ambient” architecture. Onboarding your applications onto a service mesh with ambient mode is now as easy as labeling a namespace. Your applications will gain instant benefits such as mTLS with cryptographic identity for mesh traffic and L4 observability. If you need to control access or routes or increase resiliency or gain L7 metrics among your applications in ambient mesh, you can apply waypoint proxies to your applications as needed. We’re big fans of paying for only what we need, as it not only saves resources but also saves operation cost from constantly updating many proxies! We invite you to try the new Istio ambient data plane architecture to experience how simple it is. We look forward to your feedback in the Istio community!