Getting Started with Ambient Mode
This guide lets you quickly evaluate Istio’s ambient mode. These steps require you to have a cluster running a supported version of Kubernetes (1.26, 1.27, 1.28, 1.29). You can install Istio ambient mode on any supported Kubernetes platform, but this guide will assume the use of kind for simplicity.
Follow these steps to get started with Istio’s ambient mode:
- Download and install
- Deploy the sample application
- Adding your application to ambient
- Secure application access
- Control traffic
- Uninstall
Download and install
Install kind
Download the latest version of Istio (v1.21.0 or later) with Alpha support for ambient mode.
Deploy a new local
kindcluster:$ kind create cluster --config=- <<EOF kind: Cluster apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4 name: ambient nodes: - role: control-plane - role: worker - role: worker EOFInstall the Kubernetes Gateway API CRDs, which don’t come installed by default on most Kubernetes clusters:
$ kubectl get crd gateways.gateway.networking.k8s.io &> /dev/null || \ { kubectl kustomize "github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/config/crd/experimental?ref=444631bfe06f3bcca5d0eadf1857eac1d369421d" | kubectl apply -f -; }Install Istio with the
ambientprofile on your Kubernetes cluster, using the version ofistioctldownloaded above:
$ istioctl install --set profile=ambient --set "components.ingressGateways[0].enabled=true" --set "components.ingressGateways[0].name=istio-ingressgateway" --skip-confirmation
After running the above command, you’ll get the following output that indicates five components (including ztunnel) have been installed successfully!
✔ Istio core installed
✔ Istiod installed
✔ CNI installed
✔ Ingress gateways installed
✔ Ztunnel installed
✔ Installation complete
$ istioctl install --set profile=ambient --skip-confirmation
After running the above command, you’ll get the following output that indicates four components (including ztunnel) have been installed successfully!
✔ Istio core installed
✔ Istiod installed
✔ CNI installed
✔ Ztunnel installed
✔ Installation complete
- Verify the installed components using the following commands:
$ kubectl get pods -n istio-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
istio-cni-node-zq94l 1/1 Running 0 2m7s
istio-ingressgateway-56b9cb5485-ksnvc 1/1 Running 0 2m7s
istiod-56d848857c-mhr5w 1/1 Running 0 2m9s
ztunnel-srrnm 1/1 Running 0 2m5s
$ kubectl get daemonset -n istio-system
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
istio-cni-node 1 1 1 1 1 kubernetes.io/os=linux 2m16s
ztunnel 1 1 1 1 1 kubernetes.io/os=linux 2m10s
$ kubectl get pods -n istio-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
istio-cni-node-d9rdt 1/1 Running 0 2m15s
istiod-56d848857c-pwsd6 1/1 Running 0 2m23s
ztunnel-wp7hk 1/1 Running 0 2m9s
$ kubectl get daemonset -n istio-system
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
istio-cni-node 1 1 1 1 1 kubernetes.io/os=linux 2m16s
ztunnel 1 1 1 1 1 kubernetes.io/os=linux 2m10s
Deploy the sample application
You’ll use the sample bookinfo application, which is part of the Istio distribution that you downloaded above. In ambient mode, you deploy applications to your Kubernetes cluster exactly the same way you would without Istio. This means that you can have your applications running in your cluster before you enable ambient mode, and have them join the mesh without needing to restart or reconfigure them.
Start the sample services:
$ kubectl apply -f @samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml@$ kubectl apply -f @samples/sleep/sleep.yaml@ $ kubectl apply -f @samples/sleep/notsleep.yaml@sleepandnotsleepare two simple applications that can serve as curl clients.Deploy an ingress gateway so you can access the bookinfo app from outside the cluster:
Create an Istio Gateway and VirtualService:
$ kubectl apply -f @samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml@
Set the environment variables for the Istio ingress gateway:
$ export GATEWAY_HOST=istio-ingressgateway.istio-system
$ export GATEWAY_SERVICE_ACCOUNT=ns/istio-system/sa/istio-ingressgateway-service-account
Create a Kubernetes Gateway and HTTPRoute:
$ sed -e 's/from: Same/from: All/'\
-e '/^ name: bookinfo-gateway/a\
namespace: istio-system\
' -e '/^ - name: bookinfo-gateway/a\
namespace: istio-system\
' @samples/bookinfo/gateway-api/bookinfo-gateway.yaml@ | kubectl apply -f -
Set the environment variables for the Kubernetes gateway:
$ kubectl wait --for=condition=programmed gtw/bookinfo-gateway -n istio-system
$ export GATEWAY_HOST=bookinfo-gateway-istio.istio-system
$ export GATEWAY_SERVICE_ACCOUNT=ns/istio-system/sa/bookinfo-gateway-istio
Test your bookinfo application. It should work with or without the gateway:
$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- curl -s "http://$GATEWAY_HOST/productpage" | grep -o "<title>.*</title>" <title>Simple Bookstore App</title>$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/ | grep -o "<title>.*</title>" <title>Simple Bookstore App</title>$ kubectl exec deploy/notsleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/ | grep -o "<title>.*</title>" <title>Simple Bookstore App</title>
Adding your application to the ambient mesh
The ambient mesh data plane relies on the ztunnel DaemonSet to redirect traffic. Check the ztunnel pods to make sure they are in a healthy state:
$ kubectl get pods -n istio-system -l app=ztunnel
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
ztunnel-29m52 1/1 Running 0 2m15s
Now you can enable all pods in a given namespace to be part of an ambient mesh by simply labeling the namespace:
$ kubectl label namespace default istio.io/dataplane-mode=ambient
Congratulations! You have successfully added all pods in the default namespace to the mesh. Note that you did not have to restart or redeploy anything!
Check the ztunnel logs to verify the proxy has received the network namespace (netns) information for an application pod in the ambient mesh, and has started proxying for it:
$ kubectl logs ds/ztunnel -n istio-system | grep -o ".*starting proxy"
... received netns, starting proxy
Now, send some test traffic:
$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- curl -s "http://$GATEWAY_HOST/productpage" | grep -o "<title>.*</title>"
<title>Simple Bookstore App</title>
$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/ | grep -o "<title>.*</title>"
<title>Simple Bookstore App</title>
$ kubectl exec deploy/notsleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/ | grep -o "<title>.*</title>"
<title>Simple Bookstore App</title>
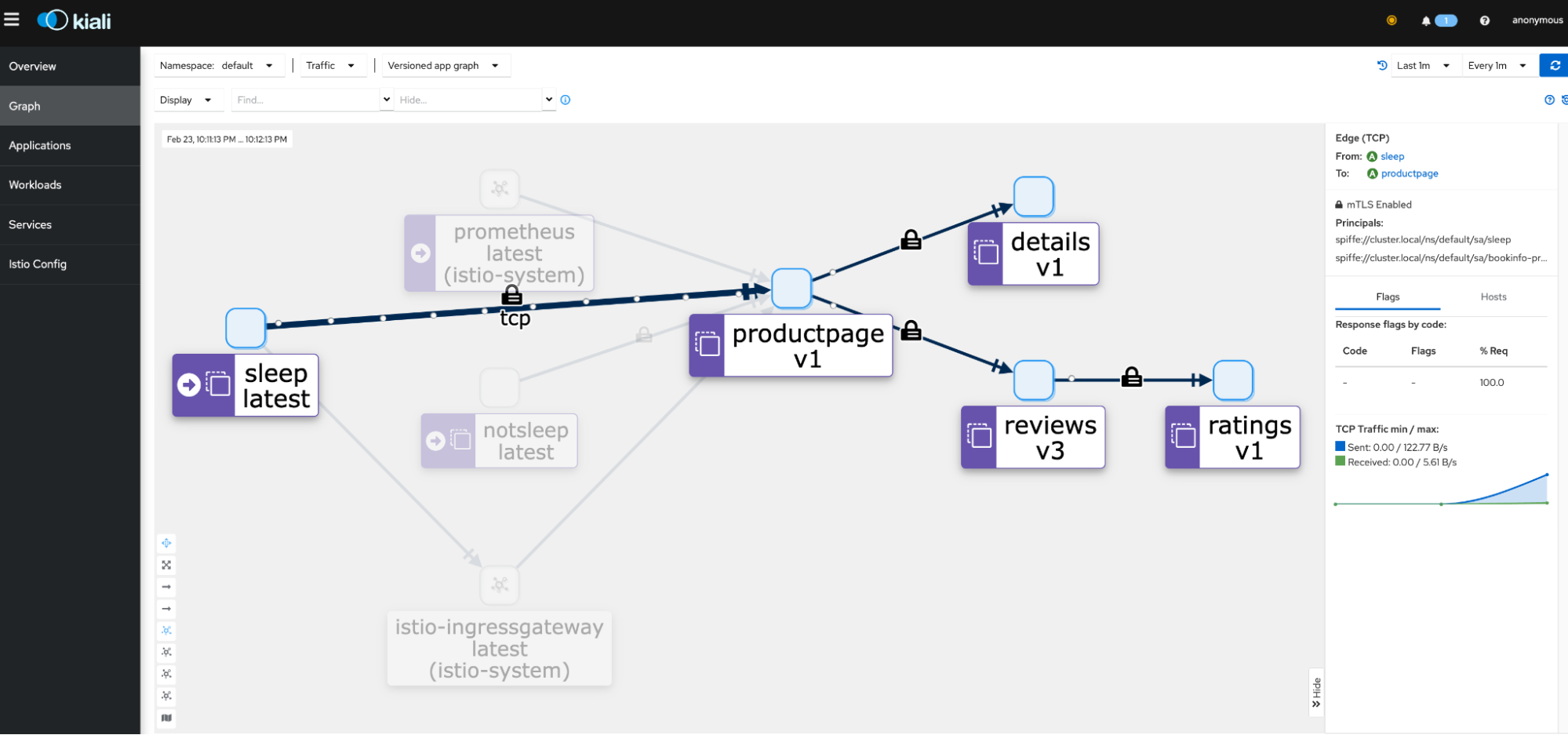
You’ll immediately gain mTLS communication and L4 telemetry among the applications in the ambient mesh. If you follow the instructions to install Prometheus and Kiali, you’ll be able to visualize your application in Kiali’s dashboard:
Secure application access
After you have added your application to an ambient mode mesh, you can secure application access using Layer 4
authorization policies. This feature lets you control access to and from a service based on client workload
identities, but not at the Layer 7 level, such as HTTP methods like GET and POST.
Layer 4 authorization policy
Explicitly allow the sleep and gateway service accounts to call the productpage service:
$ kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: productpage-viewer
namespace: default
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: productpage
action: ALLOW
rules:
- from:
- source:
principals:
- cluster.local/ns/default/sa/sleep
- cluster.local/$GATEWAY_SERVICE_ACCOUNT
EOF
Confirm the above authorization policy is working:
$ # this should succeed
$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- curl -s "http://$GATEWAY_HOST/productpage" | grep -o "<title>.*</title>"
<title>Simple Bookstore App</title>
$ # this should succeed
$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/ | grep -o "<title>.*</title>"
<title>Simple Bookstore App</title>
$ # this should fail with a connection reset error code 56
$ kubectl exec deploy/notsleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/ | grep -o "<title>.*</title>"
command terminated with exit code 56
Layer 7 authorization policy
Using the Kubernetes Gateway API, you can deploy a waypoint proxy for the productpage service that uses the bookinfo-productpage service account. Any traffic going to the productpage service will be mediated, enforced and observed by the Layer 7 (L7) proxy.
Deploy a waypoint proxy for the productpage service:
$ istioctl x waypoint apply --service-account bookinfo-productpage --wait
waypoint default/bookinfo-productpage applied
View the productpage waypoint proxy status; you should see the details of the gateway
resource with Programmed status:
$ kubectl get gtw bookinfo-productpage -o yaml
...
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2023-02-24T03:22:43Z"
message: Resource programmed, assigned to service(s) bookinfo-productpage-istio-waypoint.default.svc.cluster.local:15008
observedGeneration: 1
reason: Programmed
status: "True"
type: Programmed
Update your AuthorizationPolicy to explicitly allow the sleep and gateway service accounts to GET the productpage service, but perform no other operations:
$ kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: productpage-viewer
namespace: default
spec:
targetRef:
kind: Gateway
group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
name: bookinfo-productpage
action: ALLOW
rules:
- from:
- source:
principals:
- cluster.local/ns/default/sa/sleep
- cluster.local/$GATEWAY_SERVICE_ACCOUNT
to:
- operation:
methods: ["GET"]
EOF
$ # this should fail with an RBAC error because it is not a GET operation
$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- curl -s "http://$GATEWAY_HOST/productpage" -X DELETE
RBAC: access denied
$ # this should fail with an RBAC error because the identity is not allowed
$ kubectl exec deploy/notsleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/
RBAC: access denied
$ # this should continue to work
$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- curl -s http://productpage:9080/ | grep -o "<title>.*</title>"
<title>Simple Bookstore App</title>
Control traffic
Deploy a waypoint proxy for the review service, using the bookinfo-review service account, so that any traffic going to the review service will be mediated by the waypoint proxy.
$ istioctl x waypoint apply --service-account bookinfo-reviews --wait
waypoint default/bookinfo-reviews applied
Configure traffic routing to send 90% of requests to reviews v1 and 10% to reviews v2:
$ kubectl apply -f @samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-reviews-90-10.yaml@
$ kubectl apply -f @samples/bookinfo/networking/destination-rule-reviews.yaml@
$ kubectl apply -f @samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo-versions.yaml@
$ kubectl apply -f @samples/bookinfo/gateway-api/route-reviews-90-10.yaml@
Confirm that roughly 10% of the traffic from 100 requests goes to reviews-v2:
$ kubectl exec deploy/sleep -- sh -c "for i in \$(seq 1 100); do curl -s http://$GATEWAY_HOST/productpage | grep reviews-v.-; done"
Uninstall
Remove the label instructing Istio to enroll applications in the default namespace into the ambient mesh. It is not removed by istioctl during uninstall.
$ kubectl label namespace default istio.io/dataplane-mode-
With the label removed, we can check the logs once again to verify the proxy removal:
$ kubectl logs ds/ztunnel -n istio-system | grep inpod
Found 3 pods, using pod/ztunnel-jrxln
inpod_enabled: true
inpod_uds: /var/run/ztunnel/ztunnel.sock
inpod_port_reuse: true
inpod_mark: 1337
2024-03-26T00:02:06.161802Z INFO ztunnel::inpod::workloadmanager: handling new stream
2024-03-26T00:02:06.162099Z INFO ztunnel::inpod::statemanager: pod received snapshot sent
2024-03-26T00:41:05.518194Z INFO ztunnel::inpod::statemanager: pod WorkloadUid("7ef61e18-725a-4726-84fa-05fc2a440879") received netns, starting proxy
2024-03-26T00:50:14.856284Z INFO ztunnel::inpod::statemanager: pod delete request, draining proxy
To remove waypoint proxies, installed policies, and uninstall Istio:
$ istioctl experimental waypoint delete --all
$ istioctl uninstall -y --purge
$ kubectl delete namespace istio-system
To delete the Bookinfo sample application and its configuration, see Bookinfo cleanup.
To remove the sleep and notsleep applications:
$ kubectl delete -f @samples/sleep/sleep.yaml@
$ kubectl delete -f @samples/sleep/notsleep.yaml@
If you installed the Gateway API CRDs, remove them:
$ kubectl kustomize "github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/config/crd/experimental?ref=444631bfe06f3bcca5d0eadf1857eac1d369421d" | kubectl delete -f -