Visualizing Your Mesh
This task shows you how to visualize different aspects of your Istio mesh.
As part of this task, you install the Kiali add-on and use the web-based graphical user interface to view service graphs of the mesh and your Istio configuration objects. Lastly, you use the Kiali Public API to generate graph data in the form of consumable JSON.
This task uses the Bookinfo sample application as the example throughout.
Before you begin
Create a secret
Create a secret in your Istio namespace with the credentials that you use to authenticate to Kiali.
First, define the credentials you want to use as the Kiali username and passphrase:
$ KIALI_USERNAME=$(read -p 'Kiali Username: ' uval && echo -n $uval | base64)
$ KIALI_PASSPHRASE=$(read -sp 'Kiali Passphrase: ' pval && echo -n $pval | base64)
If you are using the Z Shell, zsh, use the following to define the credentials:
$ KIALI_USERNAME=$(read '?Kiali Username: ' uval && echo -n $uval | base64)
$ KIALI_PASSPHRASE=$(read -s "?Kiali Passphrase: " pval && echo -n $pval | base64)
To create a secret, run the following commands:
$ NAMESPACE=istio-system
$ kubectl create namespace $NAMESPACE
$ cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: kiali
namespace: $NAMESPACE
labels:
app: kiali
type: Opaque
data:
username: $KIALI_USERNAME
passphrase: $KIALI_PASSPHRASE
EOF
Install Via Helm
Once you create the Kiali secret, follow
the Helm install instructions to install Kiali via Helm.
You must use the --set kiali.enabled=true option when you run the helm command, for example:
$ helm template --set kiali.enabled=true install/kubernetes/helm/istio --name istio --namespace istio-system > $HOME/istio.yaml
$ kubectl apply -f $HOME/istio.yaml
Once you install Istio and Kiali, deploy the Bookinfo sample application.
Running on OpenShift
When Kiali runs on OpenShift it needs access to some OpenShift specific resources in order to function properly, which can be done using the following commands after Kiali has been installed:
$ oc patch clusterrole kiali -p '[{"op":"add", "path":"/rules/-", "value":{"apiGroups":["apps.openshift.io"], "resources":["deploymentconfigs"],"verbs": ["get", "list", "watch"]}}]' --type json
$ oc patch clusterrole kiali -p '[{"op":"add", "path":"/rules/-", "value":{"apiGroups":["project.openshift.io"], "resources":["projects"],"verbs": ["get"]}}]' --type json
$ oc patch clusterrole kiali -p '[{"op":"add", "path":"/rules/-", "value":{"apiGroups":["route.openshift.io"], "resources":["routes"],"verbs": ["get"]}}]' --type json
Generating a service graph
To verify the service is running in your cluster, run the following command:
$ kubectl -n istio-system get svc kialiTo determine the Bookinfo URL, follow the instructions to determine the Bookinfo ingress
GATEWAY_URL.To send traffic to the mesh, you have three options
Visit
http://$GATEWAY_URL/productpagein your web browserUse the following command multiple times:
$ curl http://$GATEWAY_URL/productpageIf you installed the
watchcommand in your system, send requests continually with:$ watch -n 1 curl -o /dev/null -s -w %{http_code} $GATEWAY_URL/productpage
To open the Kiali UI, execute the following command in your Kubernetes environment:
$ kubectl -n istio-system port-forward $(kubectl -n istio-system get pod -l app=kiali -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') 20001:20001Visit http://localhost:20001/kiali/console in your web browser.
To log into the Kiali UI, go to the Kiali login screen and enter the username and passphrase stored in the Kiali secret.
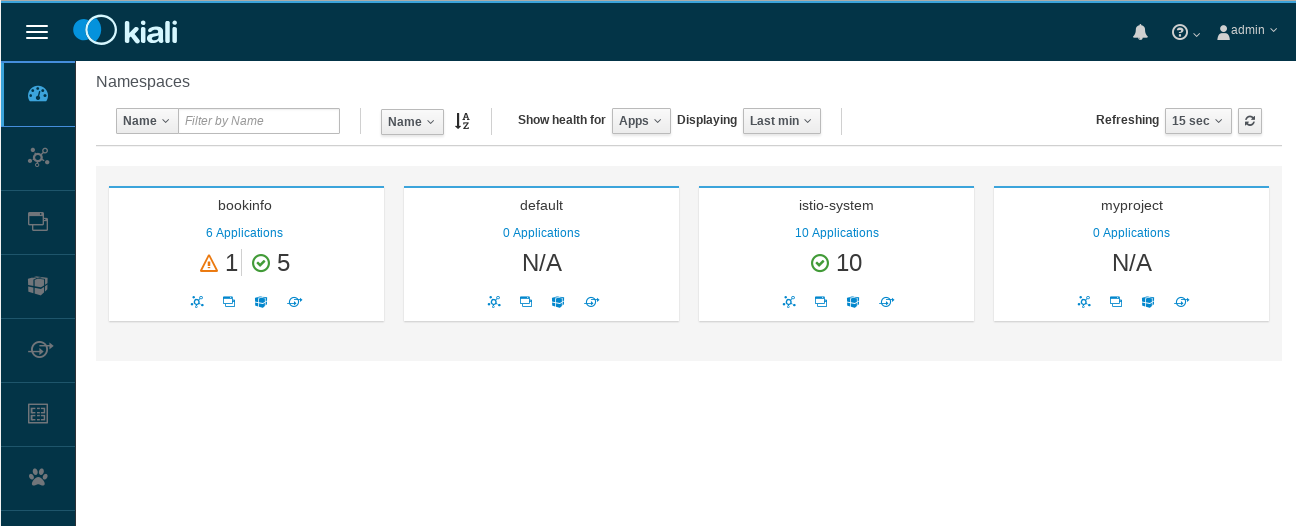
View the overview of your mesh in the Overview page that appears immediately after you log in. The Overview page displays all the namespaces that have services in your mesh. The following screenshot shows a similar page:
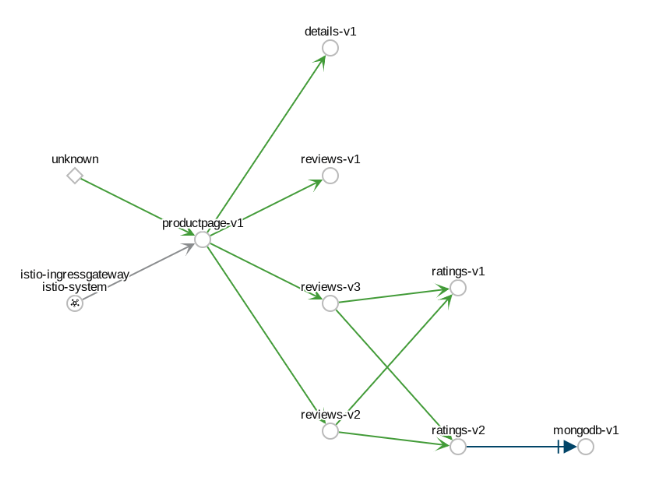
Example Overview To view a namespace graph, click on the
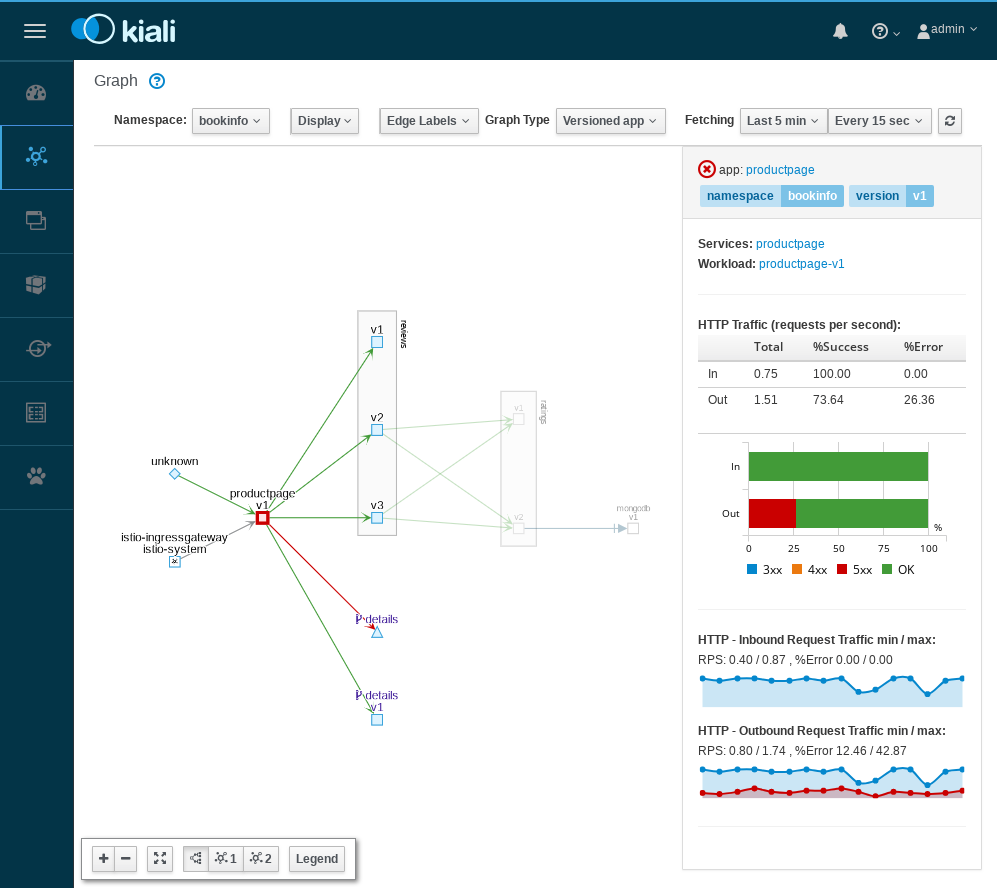
bookinfograph icon in the Bookinfo namespace card. The graph icon is in the lower left of the namespace card and looks like a connected group of circles. The page looks similar to:Example Graph To view a summary of metrics, select any node or edge in the graph to display its metric details in the summary details panel on the right.
To view your service mesh using different graph types, select a graph type from the Graph Type drop down menu. There are several graph types to choose from: App, Versioned App, Workload, Service.
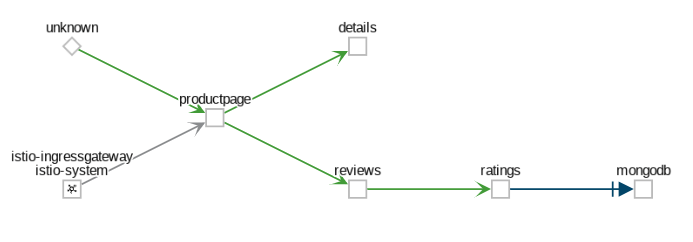
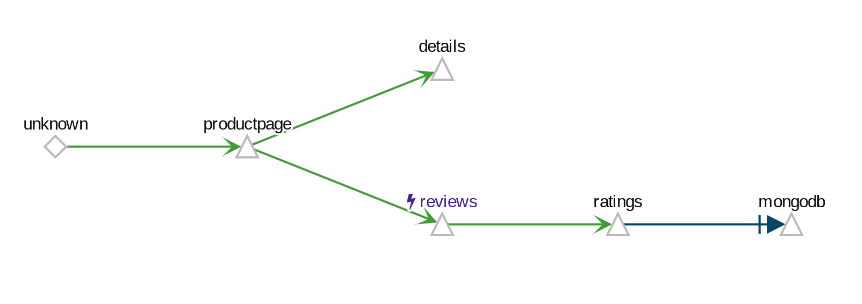
The App graph type aggregates all versions of an app into a single graph node. The following example shows a single reviews node representing the three versions of the reviews app.
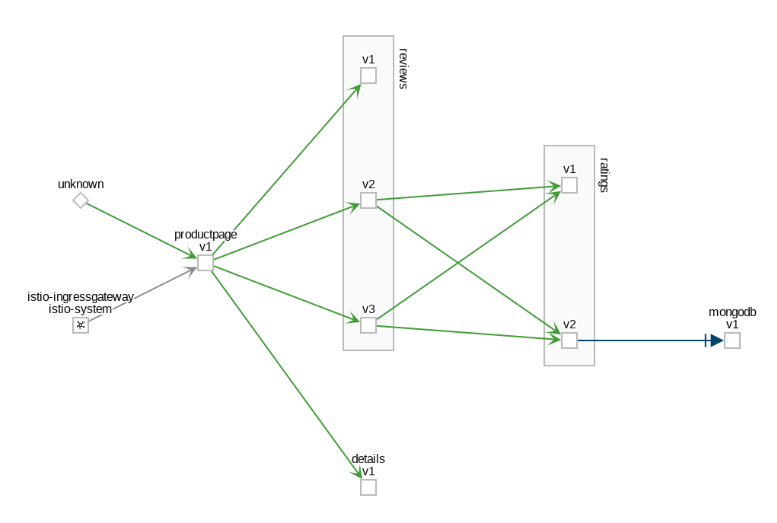
Example App Graph The Versioned App graph type shows a node for each version of an app, but all versions of a particular app are grouped together. The following example shows the reviews group box that contains the three nodes that represents the three versions of the reviews app.
Example Versioned App Graph The Workload graph type shows a node for each workload in your service mesh. This graph type does not require you to use the
appandversionlabels so if you opt to not use those labels on your components, this is the graph type you will use.Example Workload Graph The Service graph type shows a node for each service in your mesh but excludes all apps and workloads from the graph.
Example Service Graph
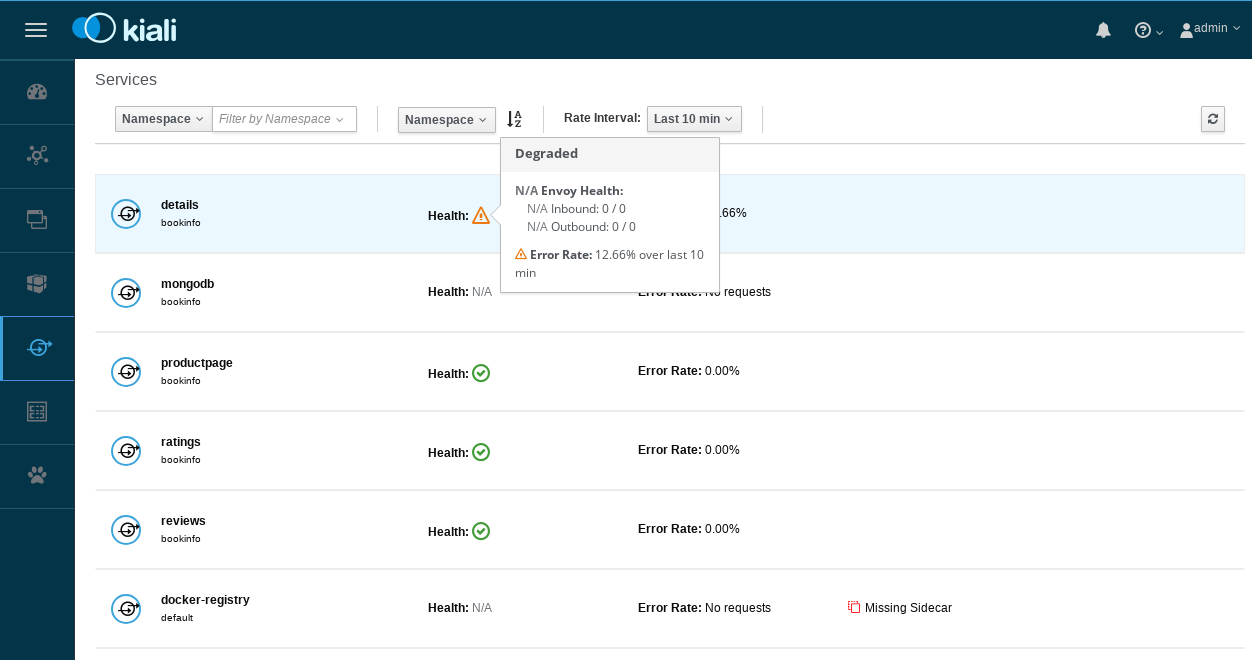
To examine the details about the Istio configuration, click on the Applications, Workloads, and Services menu icons on the left menu bar. The following screenshot shows the Bookinfo applications information:
About the Kiali Public API
To generate JSON files representing the graphs and other metrics, health, and
configuration information, you can access the
Kiali Public API.
For example, point your browser to $KIALI_URL/api/namespaces/graph?namespaces=bookinfo&graphType=app
to get the JSON representation of your graph using the app graph type.
The Kiali Public API is built on top of Prometheus queries and depends on the
standard Istio metric configuration. It also makes Kubernetes API calls to
obtain additional details about your services. For the best experience using
Kiali, use the metadata labels app and version on your application
components. As a template, the Bookinfo sample application follows this
convention.
Cleanup
If you are not planning any follow-up tasks, remove the Bookinfo sample application and Kiali from your cluster.
To remove the Bookinfo application, refer to the Bookinfo cleanup instructions.
To remove Kiali from a Kubernetes environment, remove all components with the
app=kialilabel:
$ kubectl delete all,secrets,sa,configmaps,deployments,ingresses,clusterroles,clusterrolebindings,virtualservices,destinationrules,customresourcedefinitions --selector=app=kiali -n istio-system